Implementing Zero Trust Security: A Comprehensive Guide for Modern Organizations
Implementing Zero Trust Security: A Comprehensive Guide for Modern Organizations
The traditional security perimeter has dissolved. With remote work, cloud adoption, and sophisticated cyber threats becoming the norm, organizations need a new approach to security. Enter Zero Trust – a security model that assumes breach and verifies every request as though it originates from an open network.
What is Zero Trust Security?
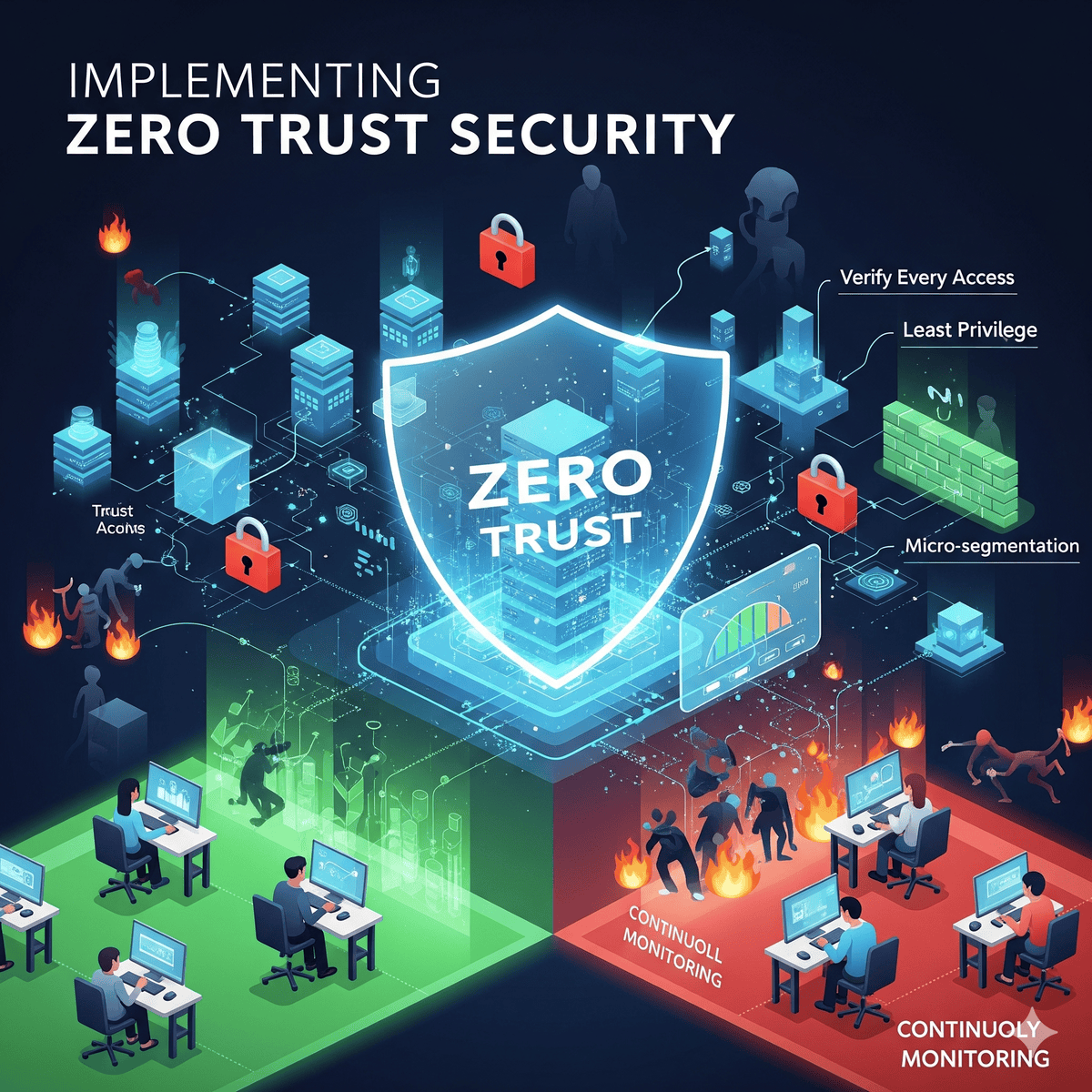
Zero Trust is a strategic approach to cybersecurity that secures an organization by eliminating trust from the network architecture. It operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify” and requires verification for every person and device trying to access systems on the network.
Core Principles of Zero Trust
- Verify Explicitly: Always authenticate and authorize based on all available data points
- Use Least Privilege Access: Limit user access with Just-In-Time and Just-Enough-Access principles
- Assume Breach: Minimize blast radius and segment access to prevent lateral movement
Key Components of Zero Trust Architecture
1. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Single Sign-On (SSO)
- Privileged Access Management (PAM)
- Identity governance and administration
2. Network Segmentation
- Micro-segmentation
- Software-defined perimeters
- Network access control (NAC)
- Virtual LANs and subnets
3. Endpoint Security
- Device compliance policies
- Endpoint detection and response (EDR)
- Mobile device management (MDM)
- Certificate-based authentication
4. Data Protection
- Data loss prevention (DLP)
- Encryption at rest and in transit
- Data classification and labeling
- Rights management systems
Implementation Strategy
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning (Months 1-2)
- Current State Analysis: Audit existing security controls and identify gaps
- Asset Inventory: Catalog all users, devices, applications, and data
- Risk Assessment: Identify critical assets and potential threat vectors
- Zero Trust Roadmap: Develop a phased implementation plan
Phase 2: Identity Foundation (Months 3-4)
- Identity Provider Setup: Implement centralized identity management
- MFA Deployment: Roll out multi-factor authentication across all systems
- Access Policies: Define and implement role-based access controls
- Privileged Access: Secure administrative accounts and access
Phase 3: Network Security (Months 5-6)
- Micro-segmentation: Implement network segmentation strategies
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA): Deploy secure remote access solutions
- Network Monitoring: Enhance visibility and monitoring capabilities
- Traffic Analysis: Implement behavioral analytics for network traffic
Phase 4: Endpoint and Data Protection (Months 7-8)
- Endpoint Security: Deploy advanced endpoint protection
- Data Classification: Implement data discovery and classification
- Encryption: Ensure comprehensive data encryption
- DLP Policies: Deploy data loss prevention controls
Common Challenges and Solutions
Challenge: Legacy System Integration
Solution: Implement zero trust principles gradually, starting with new systems and cloud environments while developing migration strategies for legacy infrastructure.
Challenge: User Experience Impact
Solution: Design seamless authentication experiences using SSO, adaptive authentication, and user behavior analytics to minimize friction.
Challenge: Complexity Management
Solution: Start with high-value assets and critical users, then expand gradually. Use automation and orchestration to manage complexity.
Measuring Zero Trust Success
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Security Incidents: Reduction in successful breaches and lateral movement
- Time to Detection: Faster identification of security events
- User Productivity: Minimal impact on user experience and productivity
- Compliance: Improved regulatory compliance and audit results
Metrics to Track
- Mean time to detect (MTTD) security incidents
- Mean time to respond (MTTR) to threats
- Number of privileged access violations
- User authentication success rates
- Network segmentation effectiveness
How Managed SOC Services Support Zero Trust
Implementing Zero Trust requires 24/7 monitoring and rapid response capabilities. Our Managed SOC services provide:
- Continuous Monitoring: Real-time visibility across your Zero Trust architecture
- Threat Detection: Advanced analytics to identify anomalous behavior
- Incident Response: Rapid containment and remediation of security incidents
- Compliance Reporting: Detailed reports demonstrating Zero Trust effectiveness
Best Practices for Zero Trust Implementation
- Start Small: Begin with a pilot program focusing on critical assets
- Prioritize Identity: Strong identity management is the foundation of Zero Trust
- Automate Where Possible: Use automation to reduce complexity and human error
- Monitor Everything: Implement comprehensive logging and monitoring
- Regular Testing: Conduct regular penetration testing and security assessments
- Employee Training: Educate users about new security policies and procedures
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and update Zero Trust policies
The Future of Zero Trust
Zero Trust is not a destination but a journey. As threats evolve and technology advances, Zero Trust architectures must adapt. Key trends to watch include:
- AI-Enhanced Security: Machine learning for behavioral analysis and threat detection
- Cloud-Native Zero Trust: Purpose-built cloud security architectures
- IoT Integration: Extending Zero Trust principles to Internet of Things devices
- Quantum-Safe Security: Preparing for quantum computing threats
Conclusion
Zero Trust represents a fundamental shift in how organizations approach cybersecurity. While implementation requires careful planning and significant effort, the benefits – reduced risk, improved compliance, and enhanced security posture – make it essential for modern organizations.
Ready to start your Zero Trust journey? Our security experts can help you assess your current environment, develop an implementation roadmap, and provide ongoing support through our Managed SOC services.
Need help implementing Zero Trust security? Contact our security experts for a free consultation and assessment of your current security posture.